WTF Solidity: 17. Library : Standing on the shoulders of giants
Twitter: @0xAA_Science | @WTFAcademy_
Community: Discord|Wechat|Website wtf.academy
Codes and tutorials are open source on GitHub: github.com/AmazingAng/WTFSolidity
In this section, we use the library contract String referenced by ERC721 as an example to introduce the library contract in solidity,
and then summarize the commonly used library functions.
Library Functions
A library function is a special contract that exists to improve the reusability of solidity and reduce gas consumption.
Library contracts are generally a collection of useful functions (library functions),
which are created by the masters or the project party.
We only need to stand on the shoulders of giants and use those functions.

It differs from ordinary contracts in the following points:
- State variables are not allowed
- Cannot inherit or be inherited
- Cannot receive ether
- Cannot be destroyed
String Library Contract
String Library Contract is a code library that converts a uint256 to the corresponding string type. The sample code is as follows:
library Strings {
bytes16 private constant _HEX_SYMBOLS = "0123456789abcdef";
/**
* @dev Converts a `uint256` to its ASCII `string` decimal representation.
*/
function toString(uint256 value) public pure returns (string memory) {
// Inspired by OraclizeAPI's implementation - MIT licence
// https://github.com/oraclize/ethereum-api/blob/b42146b063c7d6ee1358846c198246239e9360e8/oraclizeAPI_0.4.25.sol
if (value == 0) {
return "0";
}
uint256 temp = value;
uint256 digits;
while (temp != 0) {
digits++;
temp /= 10;
}
bytes memory buffer = new bytes(digits);
while (value != 0) {
digits -= 1;
buffer[digits] = bytes1(uint8(48 + uint256(value % 10)));
value /= 10;
}
return string(buffer);
}
/**
* @dev Converts a `uint256` to its ASCII `string` hexadecimal representation.
*/
function toHexString(uint256 value) public pure returns (string memory) {
if (value == 0) {
return "0x00";
}
uint256 temp = value;
uint256 length = 0;
while (temp != 0) {
length++;
temp >>= 8;
}
return toHexString(value, length);
}
/**
* @dev Converts a `uint256` to its ASCII `string` hexadecimal representation with fixed length.
*/
function toHexString(uint256 value, uint256 length) public pure returns (string memory) {
bytes memory buffer = new bytes(2 * length + 2);
buffer[0] = "0";
buffer[1] = "x";
for (uint256 i = 2 * length + 1; i > 1; --i) {
buffer[i] = _HEX_SYMBOLS[value & 0xf];
value >>= 4;
}
require(value == 0, "Strings: hex length insufficient");
return string(buffer);
}
}
It mainly contains two functions, toString() converts uint256 to string,
toHexString() converts uint256 to hexadecimal, and then converts it to string.
How to use library contracts
We use the toHexString() function in String library function to demonstrate two ways of using the functions in the library contract.
1. using for command
Command using A for B can be used to attach library functions (from library A) to any type (B). After the instruction,
the function in the library A will be automatically added as a member of the B type variable,
which can be called directly. Note: When calling, this variable will be passed to the function as the first parameter:
// Using the library with the "using for"
{
using Strings for uint256;
function getString1(uint256 _number) public pure returns(string memory){
// Library functions are automatically added as members of uint256 variables
return _number.toHexString();
}
2. Called directly by the library contract name
// Called directly by the library contract name
function getString2(uint256 _number) public pure returns(string memory){
return Strings.toHexString(_number);
}
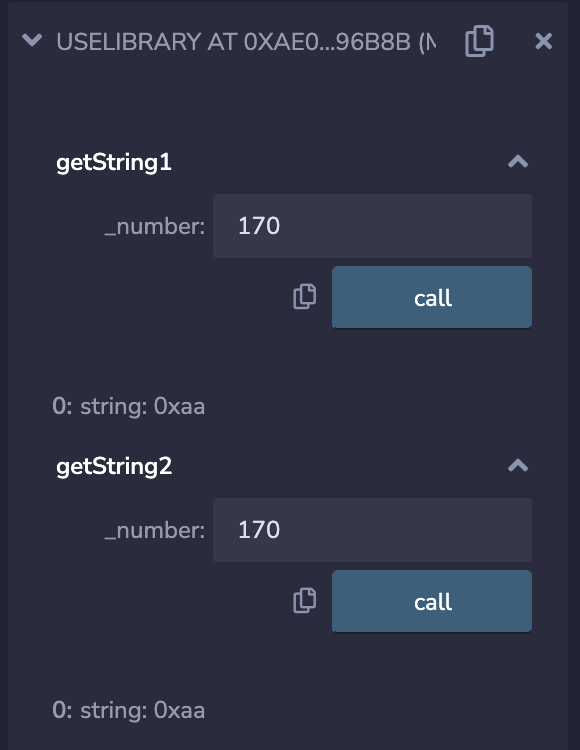
We deploy the contract and enter 170 to test,
both methods can return the correct hexadecimal string "0xaa",
proving that we call the library function successfully!
Summary
In this lecture, we use the referenced library function String of ERC721 as an example to introduce the library function (Library) in solidity.
99% of developers have no need to write library contracts themselves,
who can use the ones written by masters.
The only thing we need to know is that which library contract to use and where the library is suitable.
Some commonly used libraries are: